Temperature range: -20°C to +100°C
Humidity range: 10% r.h. to 98% r.h.
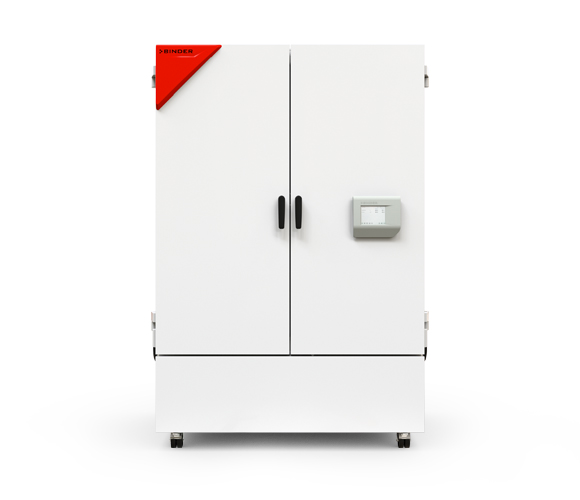
Sizes: 130 to 1600 liters in volume

ICH stability testing
Stability is one of the most important and, simultaneously, most critical quality characteristics of a medicinal product. The International Council for Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) has developed guidelines that ensure a uniform assessment of the stability of active ingredients and medicinal products. Drug authorities worldwide require stability testing in accordance with the ICH guideline Q1A (R2) to ensure the safety and efficacy of pharmaceuticals.
These tests, which can last between 12 and 60 months, provide crucial information on how active ingredients and ready-to-use drugs change over time under controlled ambient conditions. Stability testing is therefore an essential step in the approval process and plays a decisive role in determining whether a drug is approved or not.
ICH stability testing for safe drugs
The ICH Q1A guidelines form the basis of pharmaceutical quality assurance through scientifically based stability testing. They are required for the approval process and thus guarantee the safety and efficacy of drugs throughout their entire life cycle.
When is a drug considered stable?
A drug is considered stable if its chemical, physical and microbiological properties remain unchanged during storage and use by the patient and thus meet the defined requirements. The active ingredient content must not fall below a certain level. Degradation products may only be produced in minimal quantities within certain limits. The release of the active ingredient from the dosage form must not change adversely during storage.
ICH stability testing determines how the quality of an active ingredient or drug changes under the influence of temperature, humidity and light. In addition, these tests help to determine the appropriate conditions and time frames for storage and use.
From laboratory to market maturity
The path to approval for a drug is a strictly regulated process. The stability data are recorded and submitted to the regulatory authority as part of the approval application, together with information on the shelf life and storage conditions.
Stability testing is also carried out after approval to ensure that the specified stability criteria are met throughout the product’s shelf life. This continuous quality control ensures that drugs retain their efficacy and safety from development to final consumption.
Test conditions and parameter

For the storage of drugs for stability testing, the storage conditions, i.e. temperature and relative humidity, are specified by the ICH guidelines:
- Long-term stability tests: Storage at 25 ± 2°C and 60 ± 5% r.h. or 30 ± 2°C and 65 ± 5% r.h. for the duration of the repeat testing period of the active ingredient or for the proposed expiration date of the product to define or confirm shelf life. The test lasts at least 12 months and up to 60 months.
- Intermediate stability testing: Storage under conditions that lead to a moderate increase in the rate of chemical degradation and physical changes, for instance at 30°C/65% r.h. for storage conditions at 25°C.
- Accelerated stability testing: Storage under intensified storage conditions aimed at increasing the rate of chemical degradation or physical change of an active ingredient or drug.
Examination parameters
Various parameters are monitored during the stability tests, including:
- Physical stability: Homogeneity of the drug
- Chemical stability: Active ingredient content and degradation products
- Microbiological stability: Test for microbiological contamination
- Packaging materials: Interactions between drugs and packaging
Procedure for ICH stability tests
- Sample preparation: Drug batches are selected, prepared for analysis and labeled.
- Determination of test conditions: The storage conditions are defined in accordance with the ICH guidelines. Typical storage conditions are as follows:
- Long-term stability tests at 25°C and 60% r.h.
- Accelerated stability tests at 40°C and 75% r.h.
- Intermediate tests at 30°C and 65% r.h.
- Test plan and time intervals : A detailed test plan determines at which points in time (e.g. after 0, 3, 6, 9, 12 months) the samples are taken and analyzed. If the samples no longer meet the predetermined stability criteria, the samples concerned might no longer be stable.
- Performance of the stability test: The samples are stored in climate chambers that precisely simulate the defined ambient conditions (temperature and relative humidity). Samples are taken and analyzed at the specified test times.
- Analytical methods: Validated analytical methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC) or mass spectrometry (MS) are used to analyze chemical changes and determine the content of active ingredients and the presence of degradation products.
- Documentation: The results are compiled and evaluated in a detailed report. The test conditions must be reproducible at all times, even after the tests have been completed.
- Quality control: Regular calibration and maintenance of the measuring devices as well as repeat tests ensure that the measurement results are reliable and reproducible.
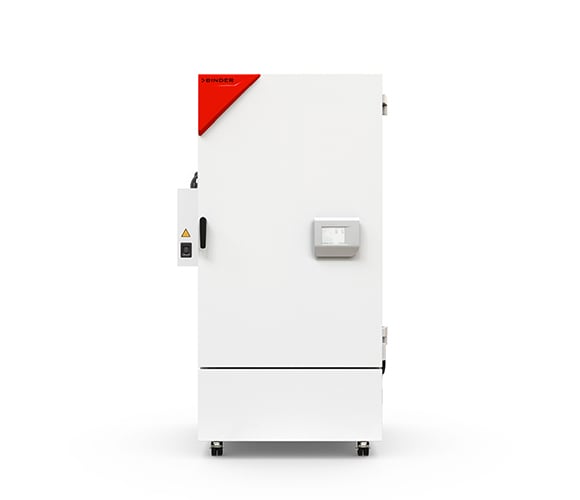
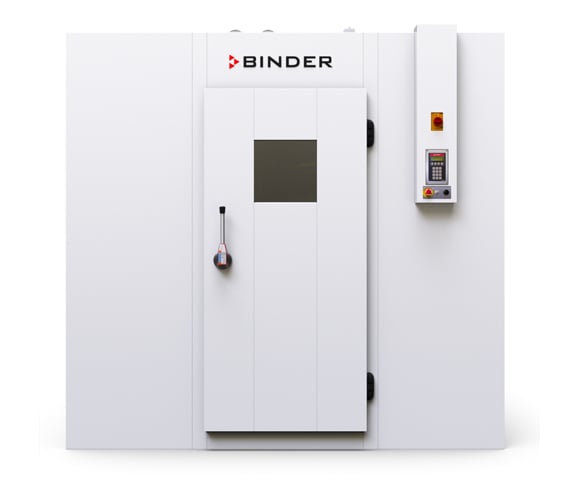
Climate chambers for ICH stability testing
The stability tests are carried out in special climate chambers, which serve as precision-controlled environments for storage of drug samples. These climate chambers enable precise control and monitoring of temperature, relative humidity and, if necessary, other ambient parameters such as light intensity. The homogeneity of the climate parameters, temperature and humidity is absolutely crucial, and safe and reliable continuous operation of the climate chamber is essential if ICH stability testing is to be carried out successfully.
The most important features of ICH climate chambers include:
- Precise and homogeneous climate conditions: Modern climate chambers guarantee homogeneous climate conditions in terms of time and space, thereby meeting the requirements of the ICH guidelines.
- Automatic data recording: The set parameters are logged continuously, enabling full documentation.
- Regular calibration and maintenance: The chambers are validated and calibrated regularly to ensure measurement accuracy.
- Flexible test environments: The units have a wide temperature and humidity range and are capable of simulating different storage conditions.
Climate chambers from BINDER – the best solution for standard-compliant ICH stability testing
Humidity test chambers
Photostability test chambers
Walk-in chambers
Documentation of ICH stability testing
It is essential that the framework conditions and the interpretation of the results are fully and comprehensibly documented in order to meet the regulatory requirements. As a result, the documentation requirements are stringent.
- Study report:
Before the tests begin, a detailed protocol is drawn up in which all test conditions, test intervals and methods used are specified. - Collection and evaluation of data:
All results are documented – from raw data to interim reports and statistical evaluations. This forms the basis for the final assessment of product stability. - Audit trail und electronic data capture:
All data changes are recorded, resulting in a seamless audit trail. This ensures the integrity and traceability of the results. - Final report:
On completion of the stability studies, a comprehensive report is drawn up summarizing all the test results and providing recommendations regarding shelf life and optimal storage conditions. - Regulatory compliance:
All documentation must comply with ICH guidelines as well as national and international regulations. This is crucial in terms of securing approval and market access for the drug.
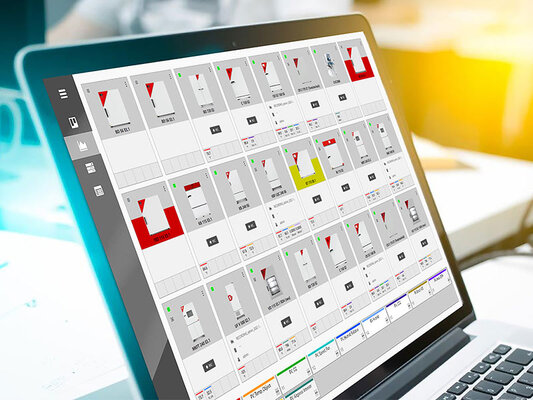
Multi Management Software APT-COM™ - standard-compliant and legally compliant
The GLP version of the Multi Management Software APT-COM™4 guarantees tamper-proof FDA and GLP-compliant documentation.
In addition to the basic unit overview, it also has an alarm center. Alarms for individual tolerance ranges or time delays are configured and saved for each individual unit. If the set parameters are exceeded or not reached, this is immediately detected by the software and the affected process is highlighted in the unit overview.


